Originally shared by Pierre Markuse
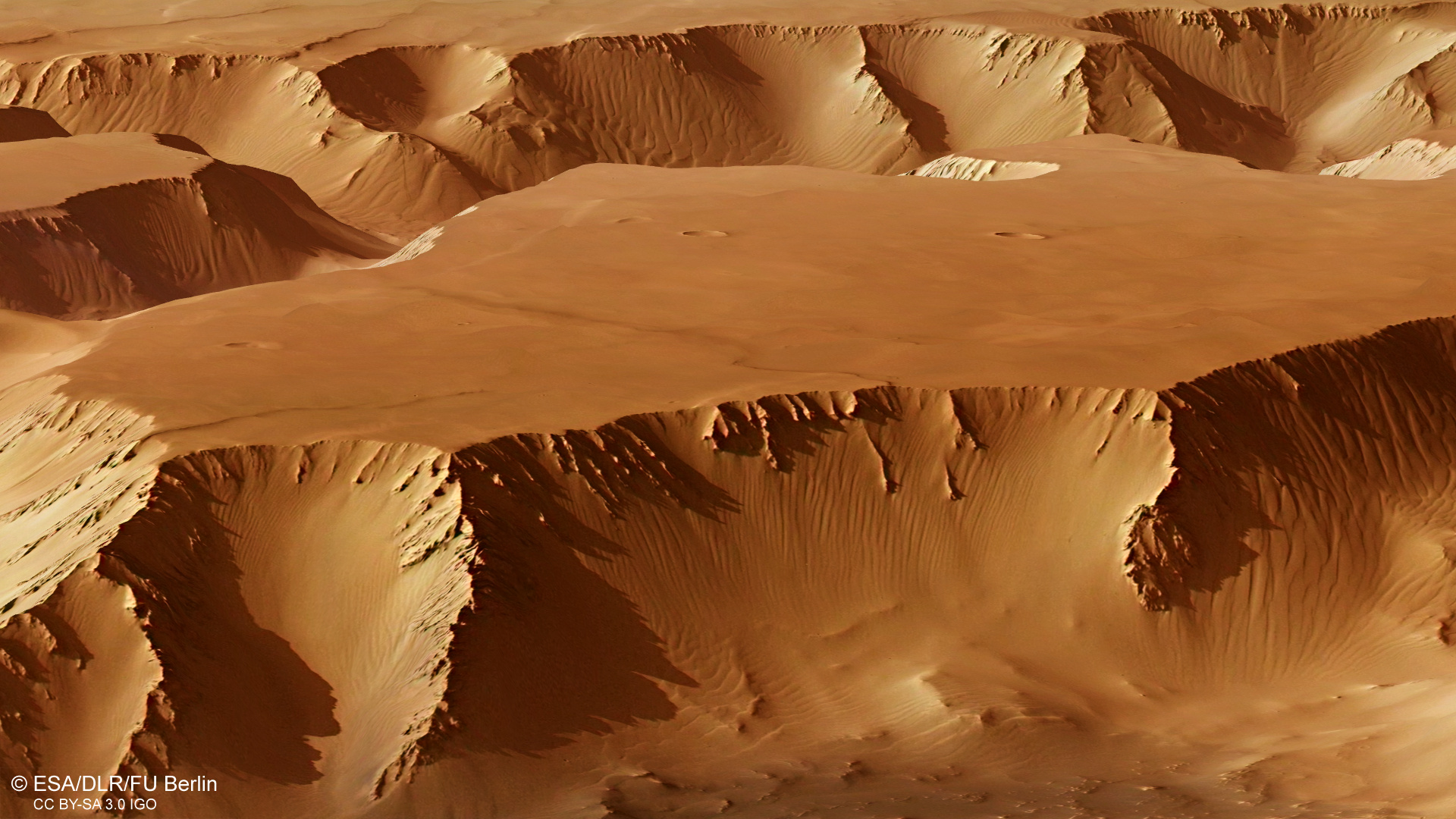
Perspective view in Noctis Labyrinthus
In this image taken on 15 July 2015 by the High-Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) aboard ESA’s Mars Express you can see a perspective view in Noctis Labyrinthus on Mars. Visible are details of landslides in the steep-sided walls of the flat-topped graben (https://goo.gl/Rma96b) in the foreground, and in the valley walls in the background. Image resolution is about 16 meters per pixel.
Read more on Noctis Labyrinthus:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Noctis_Labyrinthus
http://www.esa.int/spaceinimages/Images/2016/01/Perspective_view_in_Noctis_Labyrinthus
More on the Mars Express orbiter and the High Resolution Stereo Camera:
http://sci.esa.int/mars-express/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mars_Express
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/High_Resolution_Stereo_Camera
Image credit: Title Perspective view in Noctis Labyrinthus ESA/DLR/FU Berlin http://goo.gl/AN7tsu CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO https://goo.gl/YgMSmb
#science #mars #marsexpress #esa #NoctisLabyrinthus #hrsc #space #spacetechnology #spaceexploration


